Glucose Tolerance Test
Synonym - Specimen - Reference Value - Method - Description - Types of Glucose tolerance test and its interpretation.
Synonym : GGT
Specimen : Plasma (1 mL) collected in sodium fluoride tubes
Serum (1 mL), Plasma collected in heparin tube is also acceptable .
It is important to use the same type of collection container throughout the
entire test .
Reference Value : Fasting sample less than 120 mg/dL : 1- hour sample Less than 160
mg/dL
Method : Spectrophotometry
Description : Glucose tolerance test is indicated in case of deviation in normal
Carbohydrate metabolism as in diagnosis of diabetes millitus .
Types of Glucose tolerance test
1 - Intravenous tolerance test
2 - Oral tolerance test
Explain
Intravenous or oral tolerance tests may be used to detect glucose tolerance with persistent hyperglycemia below the renal threshold (i.e without glucosuria ).
If diabetes mellitus has been confirmed , the intravenous GTT combined with measurement of insulin after glucose injection may be used to identify the type of diabetes mellitus .
The most common use of oral GTT is to evaluate intestinal absorption
GTT may be indicated in case of hyperinsulinisim .
Glucose tolerance is determined by elevated the concentration of blood glucose at specific time before and after the oral or intravenous administration of a given quantity of glucose
GTT may be oral glucose tolerance test or intravenous glucose tolerance test , both may be used .
The oral GTT is used for individuals who are not know to have problems with gastrointestinal malabsorption . The intravenous GTT is used for individuals who are unable to tolerate oral glucose .
when glucose is given by the oral route , alteration of blood glucose concentration takes 3 phases as follow :
1 - phase one : occurs during absorption period . The rate of glucose absorption into circulation exceeds that of removal and blood glucose concentration increase .
2 - Phase two : hepatic output is inhibited and insulin secretion is stimulated .The peak level of glucose is reached and then begins to fall in which rate of removal exceeds that of entry .
3 - Phase three : glucose level reach to original values .
2 - Oral tolerance test
Explain
Intravenous or oral tolerance tests may be used to detect glucose tolerance with persistent hyperglycemia below the renal threshold (i.e without glucosuria ).
If diabetes mellitus has been confirmed , the intravenous GTT combined with measurement of insulin after glucose injection may be used to identify the type of diabetes mellitus .
The most common use of oral GTT is to evaluate intestinal absorption
GTT may be indicated in case of hyperinsulinisim .
Glucose tolerance is determined by elevated the concentration of blood glucose at specific time before and after the oral or intravenous administration of a given quantity of glucose
GTT may be oral glucose tolerance test or intravenous glucose tolerance test , both may be used .
The oral GTT is used for individuals who are not know to have problems with gastrointestinal malabsorption . The intravenous GTT is used for individuals who are unable to tolerate oral glucose .
Oral glucose tolerance test
when glucose is given by the oral route , alteration of blood glucose concentration takes 3 phases as follow :
1 - phase one : occurs during absorption period . The rate of glucose absorption into circulation exceeds that of removal and blood glucose concentration increase .
2 - Phase two : hepatic output is inhibited and insulin secretion is stimulated .The peak level of glucose is reached and then begins to fall in which rate of removal exceeds that of entry .
3 - Phase three : glucose level reach to original values .
Procedure
1 - Take fasting blood sample .
2 - 2.2 g of glucose / Kg body weight are given orally
3 - Take blood samples at 30 - 60 min. intervals for 3 - 4 hours .
Interpretation
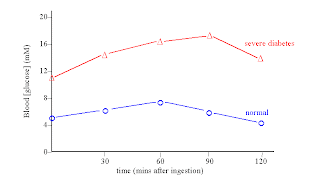
1 - In diabetic patients, fasting blood glucose usually more than 120 mg/dl and the level exceeds 180 mg/dl during testing by 30-60 min. and not returns to the resting level again . Prolonged glucose disappearance indicates intolerance
as in diabetes mellitus , hyperadrenocorticism , hyperthyroidism , and hepatic insufficiency .
2 - Normally , fasting blood glucose is less than 120 mg/ dl , and values , not exceeds 160 mg/dl during testing (1 st hour ) , then the level return to normal by the end of the 2nd hours .
3 - Failure to reach the maximal levels may indicate intestinal malabsorption . Lower glucose level than peak values may be seen in hypothyroidism adrenal insufficiency , hypopituitarism , and hyperinsulinism .